Here is a list of nine forest-based industries.
Any industry which depends on forests for their raw material requirement is considered to be forest or wood based industry. India is one of the leading countries with mushrooming of wood based industries which include pulp and paper, match, saw wood, veneer and plywood, pencil and dendro biomass industries.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The forest based industry is growing rapidly with the increasing demand for furniture, housing, construction material, packaging, agriculture good, sports goods, plywood, veneer, matches etc. Similarly the biomass based power generation industries are also on the raise across the country to generate electricity from forest biomass. This growing demand of wood and wood based industries will create a wood deficit of 20-70 million cubic meter by 2020.
It is estimated that approximately 40 per cent of the forest products are supplied from outside forest areas and more than 95 per cent of fuel wood and major timber requirement are obtained from outside forest areas. The following are the major forest based industries which depend heavily on forest and agroforestry plantation to meet the raw material requirement.
1. Pulp and Paper Industries:
The pulp and paper industry is one of the key industries in India and it is highly fragmented. Today, there are about 700 paper mills in India with 33 in the large scale sector. During 1990s, the per capita consumption of paper was 3.3 kg which has now escalated to 8 kg, but still lower compared to the global average of 47.7 kg. The current production of raw material for pulp and paper production is 2.76 million tons as against the demand of 5.04 million tonnes. The shortfall is as high as 45 per cent.
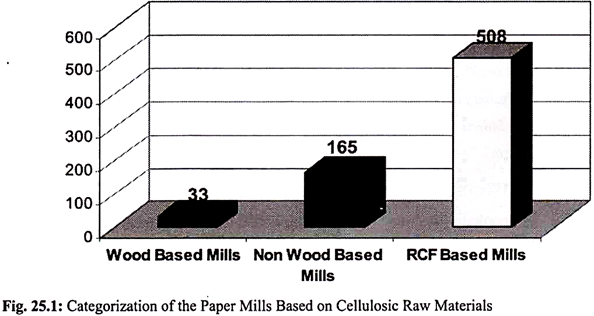
The total installed capacity of pulp & paper mills in the country is estimated to be over 7.5 million tons which is likely to increase to 14 million tons by the year 2020. In India, paper is manufactured from wide range of raw material like wood, recovered paper, baggasse and other agro residues. Based on that the paper mills have been classified and furnished in Fig. 25.1.
Currently the paper industries in the country face serious problem in terms of raw material availability which became a major deterrent to competitiveness and growth of industry. Hence all the industries have started massive plantation programme with varying degree of success.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Major Pulpwood Species:
i. Bamboo
ii. Casuarina spp.
iii. Eucalyptus spp.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
iv. Leucaena spp.
v. Acacia spp.
vi. Populus spp.
2. Match Industries:
Match wood industry is one of the oldest wood based industries in India. About 75 per cent of the total match wood industries in the country are located in the state of Tamil Nadu which comprises nearly 6,000 match industries with mechanized, semi mechanized and as cottage industry. The per capita consumption of matches in India increased steadily from 2.45 kg (1970) to 4.25 kg (1987).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The current per capita consumption rose to 6.0 kg which is more staggering. The increasing demand for the matches coupled with declining wood resources is a major bottle neck faced by the entire match industries in India including the ancillary splint and veneer industries. In fact, there was a short fall of 9,00,000 m3 in the year 2000. The veneer quality wood for match boxes, which accounts for 44 per cent of match wood used, is also in short supply.
Major Matchwood Species:
i. Ailanthus excelsa
ii. Albizia falcataria
iii. Alianthus triphysa
iv. Albizia lebbeck
v. Anthocephalus cadamba
vi. Erythrina indica
vii. Populus spp.
3. Timber and Sawn Wood Industries:
Traditionally people in the country predominantly use timber and other converted wood in all their domestic and industrial wood requirement. The rapid population growth, urbanization and industrialization resulted in greater usage of wood in furniture, housing and construction material. During, 2010-2012 more than 500 million square feet of space is estimated to be built in urban areas of the country and the wood products were valued around US Dollar 3 billion.
With greater usage wood as a predominant material for housing and construction material in urban and semi urban areas there is going to be a great demand for timber and other sawn wood requirement. The Indian furniture market is estimated at 8 billion US Dollar and in most cases raw materials are imported from various countries.
Major Timber Species:
i. Tectona grandis
ii. Terminalia spp.
iii. Albizia spp.
iv. Gmelina arborea
v. Azadirachta indica
vi. Pterocarpus spp.
vii. Mangifera indica
viii. Artocarpus spp.
ix. Dalbergia spp.
x. Dipterocarpus spp.
xi. Eugenia spp.
4. Plywood Industries:
One of the fastest growing in India is the plywood industry. The industrialization and urbanization and the increased interest on interior decorations have made great usage of plywood in the country. Wide range of species have been found amenable for making face, core and inner veneers resulted in establishment of more than 2,000 small scale industries involved in plywood manufacture.
The liberalization and privatization policy of government of India also significantly contributed towards establishment of new rural industries. These industries also depend heavily on various species which thereby attracted large scale promotion of plywood based industrial wood plantations.
Major Plywood Species:
i. Populus spp.
ii. Melia dubia
iii. Paulownia spp.
iv. Eucalyptus spp.
v. Ailanthus spp.
5. Particle Board Industries:
Particle board is reconstituted constructional panel particularly developed as a substitute for natural constructional wood and is made from low grade waste woods or from ligneous agricultural residues. These particle boards are predominantly used for wall paneling and interior decorations in domestic and industrial wood sector. In India, the first particle board industry was set up in late 1950s at Sitapur in Uttar Pradesh and from then onwards large number of industries has been installed across the country.
Major Raw Materials:
i. All types of wood waste
ii. All types of pine needles
iii. All types of Casuarina needles
iv. Ligneous agriculture residues
6. Fibre Board Industries:
Fibre board is constituted using sheet materials of widely varying diversities manufactured from refined or partially refined wood fibers or other vegetable fibers.
7. Dendro Biomass Power Generation Industries:
Biomass is an important fuel source in overall energy scenario. Biomass is produced through chemical storage of solar energy in plants and other organic matter as a result of photosynthesis. This biomass include plantation that produces energy crops, natural vegetable growth and other organic waste and residues.
Among all these biomass, the role of dendro biomass is very significant due to their higher calorific value and increased fuel efficiency. Hence, large number of dendro biomass based power plants has been established across the country to generate electricity.
Major Energy Crop:
i. Prosopis spp.
ii. Acacia spp.
iii. Albizia spp.
iv. Dalbergia sissoo
v. Leucaena leucocephala
vi. Casuarina equisetifolia
vii. Eucalyptus spp.
viii. Gliricidia spp.
ix. Ceasalpinea spp.
x. Chuckrassia spp.
xi. Other hard woods
8. Oil and Biodiesel Industries:
The demand for edible and non-edible oil is continuously on the rise due to industrial and economic development. But there is no concomitant effort to augment the production potential of oil seeds in the country. This resulted in a massive import of nearly 46 per cent of edible oil till the recent past thus claiming huge amount of country’s exchequer. Similarly the crude oil requirement in the country is also increasing due to development in transport and industrial sector.
Till the recent past the consumption of crude oil was about 184.68 million tones and the rate energy consumption is increasing at the rate of 6.5 per cent per annum. India’s share of crude oil production is about one per cent of total world crude oil production while in consumption its share is about 3.1 per cent of total world consumption which necessitated massive imports of crude oil.
The import of crude oil has increased from 63 per cent in 1971-1980 to nearly about 80 per cent in 2007-2008 which is an alarming issue for the country and warrants development of alternate renewable resources. Under such circumstances, efforts have been taken by various departments of Government of India to promote non edible oil seeds in the country to augment the vegetable oil feed stock to generate biofuel.
Simultaneously large number of private sector oil and biodiesel production industries has been established across the country but for want of sustainable raw material resource availability these industries are under great threat. This facilitated promotion of tree borne oil seeds across the country and their inclusion under farm and agroforestry system.
9. Value Addition Industries:
The wood based industries have to store the harvested raw materials during rainy season in order to have sustainable raw material availability and to sustain the industrial process during lean season. The post-harvest management of huge volume of industrial wood necessitates proper handling, storage and utilization which demand a scientific intervention in order to reduce post-harvest losses due to biological agents particularly powder post beetles and pin hole borers.
These biological agents are taking heavy toll of stored industrial raw materials which need to be addressed. Hence large number wood seasoning and preservative industries have been established to avoid post-harvest losses. Similarly, the plantation and industrial processing activities accounts for 20-30 per cent of wood residues which are either unutilized or underutilized for want of suitable recycling technologies.
These plantation and industrial wood residues have been successfully value added into briquettes and as on today many industries have been established across the country and successful value addition using plantation residues have been evidenced. These value added briquettes acted as excellent feed stock for biomass power generation industry, boiler industries and other industries requiring biomass for meeting the energy demands. The entire value addition process of plantation residues is depicted in Fig.25.2.